
Clive Bull 1am - 4am
18 May 2022, 15:05 | Updated: 18 May 2022, 15:08
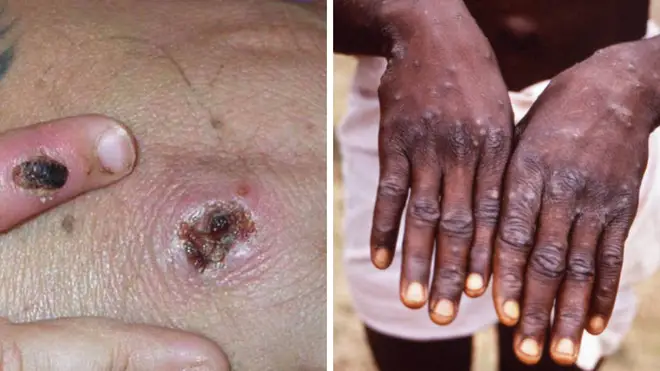
Europe has been warned to take "great care" after further cases of monkeypox were diagnosed in Spain and Portugal.
Health officials have reportedly been placed on high alert following eight suspected cases of the virus in Spain, whilst five men have tested positive in Portugal and at least a further 15 are being investigated.
Four more cases of monkeypox were identified in the UK on Sunday, bringing the total number of confirmed cases of the disease in Britain to seven.
On Tuesday Fernando Simón, director of the Centre for the Coordination of Health Alerts and Emergencies in Spain said great care must be taken adding that "it is not likely that monkeypox will generate a significant transmission but it cannot be ruled out".
Read more: Rare case of monkeypox confirmed in England as patient treated in isolation unit
UKHSA has detected four new cases of monkeypox – three in London and one in the North East of England 🧵Thread:
— UK Health Security Agency (@UKHSA) May 16, 2022
These cases do not have known connections to the previous confirmed cases announced on May 7 and May 14. Read more: https://t.co/e8jksQo9Av
The UK Health Security Agency (UKHSA) announced on Monday that three of the cases have been detected in London, and one in the North East of England,
The health agency is working to find links between the latest four cases, which all appear to have been identified in the capital.
Common contacts have been established between two of the four individuals who have caught the virus.
Those needing care are being treated in specialist infectious disease units at the Royal Free Hospital, Royal Victoria Infirmary in Newcastle upon Tyne and Guy's and St Thomas'.
UKHSA added that all four of the most recent cases self-identify as gay, bisexual or other men who have sex with men.
The health body is therefore asking these groups "to be alert" to possible symptoms, which include rashes or lesions on any part of their body, especially their genitalia, and to contact a sexual health service if they have concerns.
Read more: Monkeypox spreading in UK by 'sexual transmission', experts believe
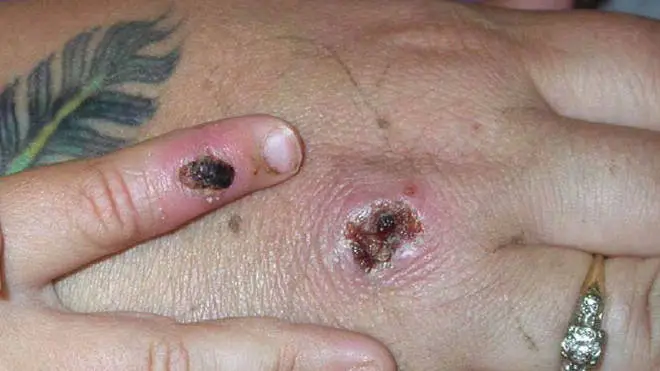
These cases do not, however, seem to be connected to the previous confirmed cases of monkeypox in the UK which were announced on May 14, nor the first UK case announced on May 7, which has led to concerns that there has been transmission of the virus in the community.
The first case was a person who had recently travelled to Nigeria, which is where they were believed to have contracted the infection, before travelling to the UK.
Due to the recent rise in case numbers and uncertainties around how some of the individuals acquired their infection, UKHSA has said it is working closely with NHS partners to establish whether there have been any more cases in recent weeks, and international partners to examine whether other countries have seen a similar rise in monkeypox.
The health agency emphasises that the virus does not spread easily between people and the risk to the UK population is low.
Dr Susan Hopkins, chief medical adviser at the UKHSA said: "This is rare and unusual.
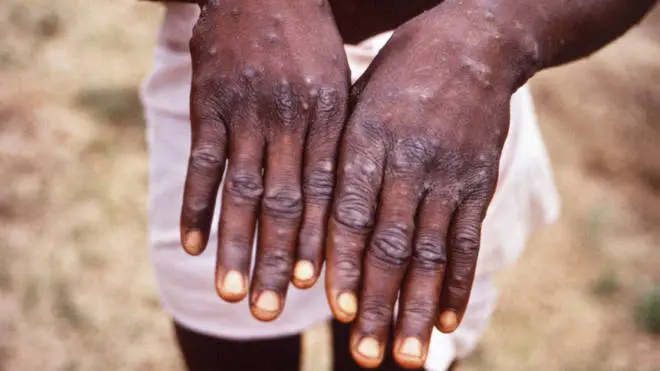
"UKHSA is rapidly investigating the source of these infections because the evidence suggests that there may be transmission of the monkeypox virus in the community, spread by close contact.
"We are particularly urging men who are gay and bisexual to be aware of any unusual rashes or lesions and to contact a sexual health service without delay.
"We are contacting any potential close contacts of the cases to provide health information and advice."
The rash, which can develop as part of the virus, changes and goes through different stages before finally forming a scab, which later falls off.
The health agency also said that initial symptoms of monkeypox include fever, headache, muscle aches, backache, swollen lymph nodes, chills and exhaustion.
The first UK case of monkeypox was recorded in September 2018 and until now had only ever been detected in four countries outside of Africa — the UK, US, Israel and Singapore.